Testing and certification
Food testing is carried out at multiple stages to ensure safety and quality throughout the production process. At the raw material stage, ingredients are examined for contaminants such as pesticides and heavy metals before entering manufacturing. During production, samples are routinely tested to monitor hygiene, microbial activity, and chemical composition. Once the product is finished, it undergoes post-production testing to verify safety, nutritional value, and labelling accuracy. Even after reaching distribution and retail, random checks by regulatory bodies or retailers help maintain ongoing compliance and consumer protection.
Food testing is vital for ensuring consumer safety by detecting harmful pathogens that can lead to foodborne illnesses. It helps prevent adulteration by identifying unsafe additives, pesticide residues, or inferior ingredients that compromise food integrity. Testing also ensures regulatory compliance with national and international standards, protecting manufacturers from fines, recalls, or legal consequences. By verifying nutritional claims, it promotes label accuracy and transparency, preventing consumers from being misled. Ultimately, food testing supports quality control and builds trust by demonstrating a commitment to safety and consistency, which strengthens brand reputation and consumer loyalty.
As per food safety regulations in India and globally, food testing is conducted in specialized laboratories accredited by regulatory bodies like FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India), ISO, and NABL (National Accreditation Board for Testing and Calibration Laboratories).
Types of Laboratory Testing Required by Regulation
Microbiological Testing
Detects harmful microorganisms to ensure food safety.

Chemical Testing
Identifies chemical composition and contaminants in food products.

Allergen Testing
Detects allergens to protect sensitive consumers.

Pesticide Residue Testing
Ensures produce is free from harmful pesticide residues.

Heavy Metal Testing
Checks for toxic metals like lead and mercury.

Nutritional Analysis
Determines accurate nutrient content for labeling and compliance.

Shelf-Life Testing
Evaluates product stability and expiry duration.
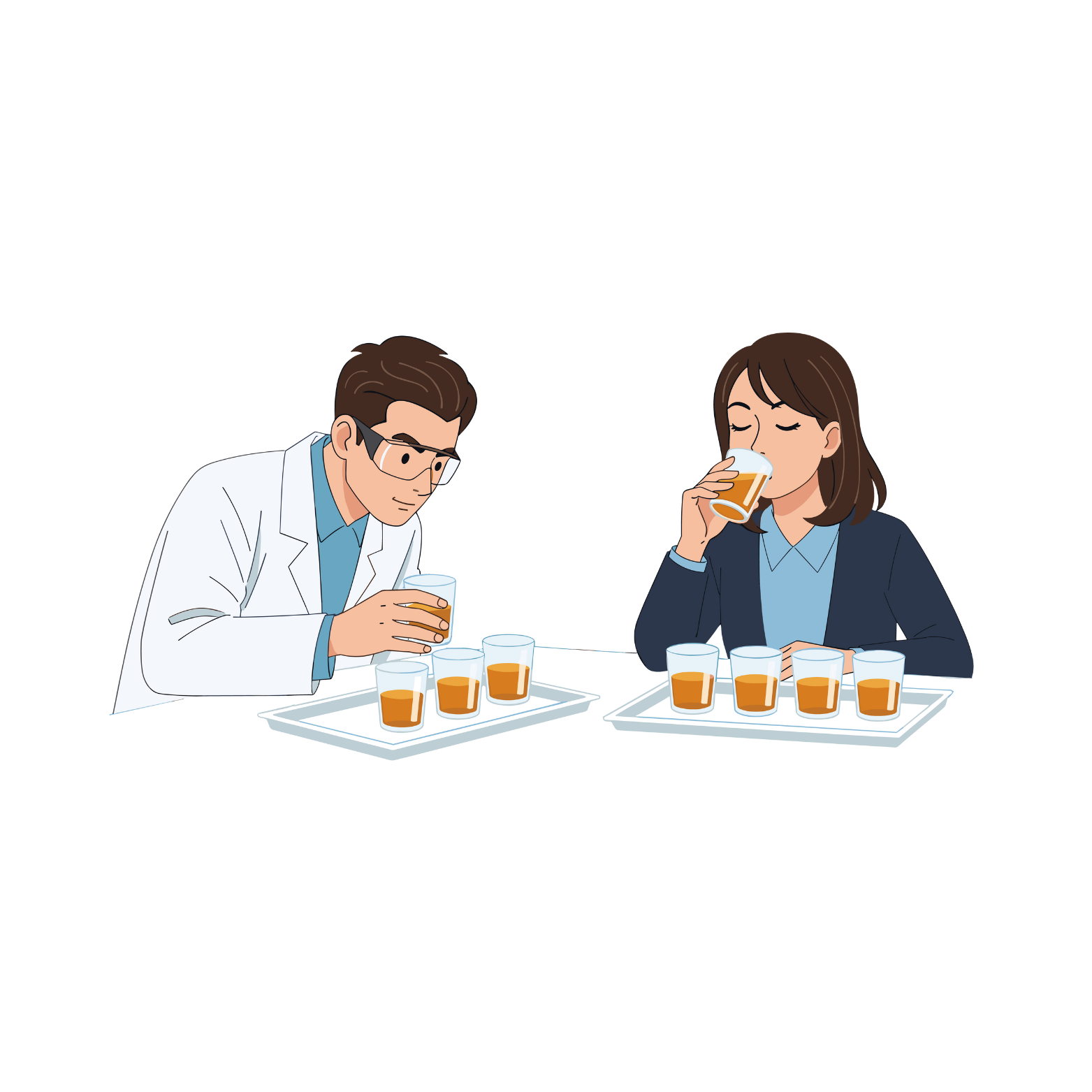

Sensory Testing
Assesses taste, aroma, texture, and overall product appeal.
Genetic Testing (DNA-based)
Verifies ingredient authenticity and detects adulteration.

Packaging Migration Testing
Ensures packaging materials don’t contaminate food.

Adulteration Testing
Detects impurities or unauthorized ingredients in products.

Physical Testing
Examines product texture, color, and physical integrity.

